1. PHASE – PHOTOSYNTHESIS PHASE
Process happening photosynthesis kloroplas passes through two phase react, which is:
1. Bright reaction
Happening if available light, let say the sun shines. Up to this phase chlorophyll at deep membrane gana absorbs red and judges light that gets long wave on spectrum light.
Energy is the capturer by chlorophyll is utilized to break down water molecule. This resolving is so-called fotolisis. Fotolisis begets water molecule break down to become hydrogen and oxygen. React fotolisis can be written by equation:
2 H 2 O 2 H 2 + O 2
H 2 one that escapes to be kept all by koenzim NADP. In this case, NADP acts as acceptor h 2 , its form is changed becomes NADPH 2 and o 2 regular in a state free.
NADP (Nikotinamida Adenin dinukleotida is Phosphate) constituting koenzim that important its role in reduction oxidation activity and there are many available in living cell. Up to that process ATP'S resultant.
2. Dark reaction
Blackman (1905) are one expert prove that reduction from CO 2 to CHO happens without light. So dark reaction is called too as blackman's reaction or CO's reduction.
If brightness reaction (Hill) and dark reaction (blackman) at merged therefore reaction it as follows:
Hill:
2 H 2 O 2 NADP H 2 + O 2
Balckman:
CO 2 + 2 NADP H 2 + O 2 2 NADP + H 2 + CO + O + H 2 + O 2
Incorporation :
2 H 2 O + CO CH 2 O + H 2 O + O 2
If this last row is multiplied 6, therefore we will get:
12 H2O + 6 CO2 (CH2O)6 + 6 H2 + 6 O2
B. Andrew and Melvin Calvin (1950) of kalifornia's university interpose CO2pada's fixation processes to take photograph sintesis / assimilation C. cycling assimilation c deep organism fotoautotrof can be figured:
Action darking to constitute CO's depreciation 2 by 2 one that took in by NADP that. In this scene, CO's depreciation 2 don't need light, so that reaction is named dark reaction.
2. PHOTOSYNTHESIS ATTEMPT
On its reality each makhuk lives to have many characteristic or basic characters. One of prima facie is living thing need food and issue rest substance. If we cermati more research, that base character leads we to at one particular mechanism which happen in the so called living thing body with metabolite.
Happening metabolite on each living thing type of course it unegual among one by another one. Compiler component dependent that living thing of level seluler until being. In metabolite process happens various chemical reaction gooding to arrange and also describe particular compound. Process that collation is so-called anabolisme, processing dsebut katabolisme's decomposition.
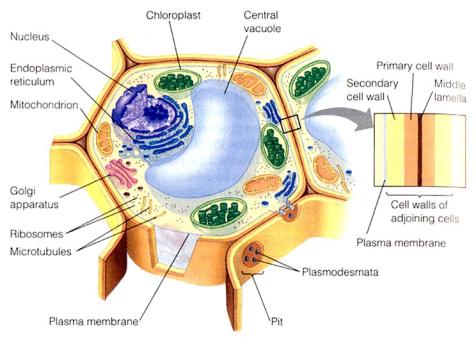
One of metabolite process example (anabolisme) one that often we hear are photosynthesis process. That process happening on botanical gets chlorophyll, correct it on pillared network / palisade and sponge on mesofil leaf / leaf flesh. On cell – palisade's cell or sponge, this process happening in one organella which is kloroplas. As has already been known, this process just happening upon there is sunlights good light and also lamplight, one that essential in light that exists white light that constitutes spectrum light of mejikuhibiniu light (jingga's red yellows appraising blue green purple). Besides sunlight, photosynthesis process also need carbon dioxide and water.
On this photosynthesis process will be resulted two compounds which is glucoses and oxygen. To know glucose content actually gets dikeahui with experimental Sact be to know oxygen content can be known by use of rib which smolder as on Ingenhouz's attempt. But then on this chance, one that we will see are not its content, but then that process speed if given by conduct that variably – difference relates temperature, light intensity, and available carbon dioxide rate.
3. FOTOSISTEM
• Fotosistem constitutes light compiler unit of tilakoid's membrane.
• Each fotosistem as complex as of protein and danjenis's protein type another molecule, including antenna which consisting of umpteen hundred pigment molecules.
• At center reacts this energy move oxidation reduction reaction.
• tereksistasi's electron of center chlorophyll reacts and be a prey to by the so called special molecule primary electron acceptor.

• Center reacts chlorophyll at oxidation with a loss electron via primary electron acceptor reduction
• Available fotosistem i. and II.
I. Fotosistem
Center chlorophyll reacts to be known by P700 because gets to catch light with wavelength 700 nm.
Fotosistem II.
Center chlorophyll reacts to be called by P680 because its absorption spectrum have top on 680 nm
4. PLANT C 3, C - 4, C AM
• Plant c 3
C3's plant
in C3's photosynthesis in contrast to C4,on C3 decarbonizes dioxida input goes to cycle
calvin directly. kloroplas's structure on C3's plant homogeneous. C3's plant
have a role is of important in metabolite, C3's plant has
low fotorespirasi ability because they don't require energy for
previous fixation. Plant C3 can lose 20 % carbon in calvin's cycle
since radiation, this plant included one of group phylogenik. Base concept reacts
no moon Calvin's cycle photosynthesis (C3) are as follows:
CO2 tied-up by RUDP hereafter is revamped as organic compound C6 that
unstable one on eventually being revamped as glucose by use of 18ATP
and 12 NADPH.Siklus this happens deep kloroplas on sectioned stroma. To
result one glucose molecule is required 6 C3's cycles.
Constitute one of alternative to settle light intensity that over
high.
naungan's application is done on agronomy that generally comprises
C3's group and also deep pembibitan's phase
On phase stocks down, all plant genus doesn't bate IC heaving full, need 30 40%, settled
with naungan
On C3's agglomerate plant, naungan not only being required on phase just stock down,
but along plant life cycle
Even with gets plant age adult, naungan's intensity gets
reduced
Naungan besides needful to reduce light intensity that gets to
subject plant, also been utilized as one of operation method
weeds
Under patron, clean slate of weeds preferably herbage
Progressively restrains from patron, weeds sprout gets quick
Compensation dot weeds herbage can be determined equal to IC on bounds
beginning available growth weeds
Growing plant at place with IC overbids from compensation dot (before
reached by saturation point), usufruct enough photosynthesis for respirasi and its rest for
growth
naungan's application impact to micro climate
Reducing IC around as big as 30 40%
Reducing airflow at surrounding coronet
Air humidity at surrounding stable more coronet (60 - 70%)
Reducing evapotranspirasi's runaway speed
Balance happening among availibility of water with level transpirasi plant
C.
• Plant c 4
C4 Meminimalkan's plant fotorespirasi's need by merges CO 2 into compound four carbons at mesofil's cell. Compound four that carbon is exported for cell to bind adit, where is detached CO2 one is utilized in Calvin's cycle.
Leaf anatomy c 4 and bands c 4:
• Plant c AM
Opening nocturnal stomatanya, merging CO 2 into organic's acid. Up to daytime, stomata is closed. CO 2 escaped from acid organic to be utilized deep Calvin's cycle.
Band c AM alike with C4's band
5. FACTOR THAT REGARDS PHOTOSYNTHESIS
1. Light intensity
Maximum photosynthesis runaway speed while there are many light.
2. Carbon dioxide concentration
More and more carbon dioxide in midair, becoming a lot of total materials that dapt
utilized by plant to pass off photosynthesis.
3. Temperature
Working enzyme in photosynthesis process just gets is conected with temperature
it is optimal. Generally fast fotosintensis increases along with at the height
temperature until enzyme tolerance bounds.
4. Water rate
Lack for water or aridity causes stomata close, constrain
carbon dioxide absorption so reduces photosynthesis runaway speed.
5. fotosintat's rate (photosynthesis result)
If fotosintat's rate as carbohydrate of dwindling, photosynthesis runaway speed will ascend.
If fotosintat's rate increases or even until saturated, photosynthesis runaway speed will
dwindling.
Growth phase
Research points out that photosynthesis runaway speed much higher on plant
one that be germinates to weigh adult plant. It may because of
plant germinates to more require a lot of energy and food for growing.